Jellyfish play a vital role in marine ecosystems. Their specific attributes attract researchers and scientists. This article will address types of jellyfish and what jellyfish eat – their diet. You’ll also learn whether they have brains and eyes. Specially designed jellyfish tanks and their difference from regular tanks are also worth learning, which you’ll find here. This article will conclude with some special jellyfish types, i.e., the largest, smallest, and venomous jellyfish species.
Content Table

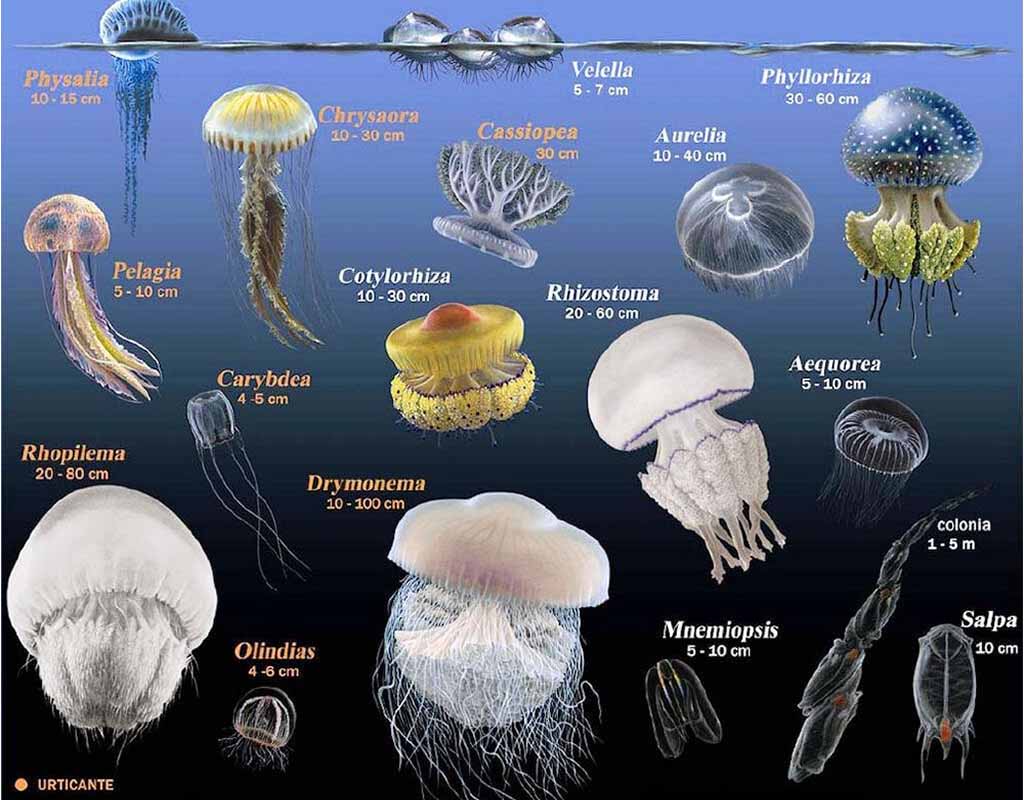
Types of Jellyfish
Scientists and researchers have discovered more than 2000 types of jellyfish. They believe that there are about 1,000 species that are still undiscovered. Many jellyfish species are almost impossible to watch, i.e., their size and transparent nature, through the naked eye. Therefore, scientists and researchers believe in such large undiscovered species.
What Do Jellyfish Eat?
Jellyfish are passive eaters. They prey and eat while floating. Moreover, Jellyfish are not picky eaters. They eat what fits in their mouth during swimming. Their food preference varies according to their size.
Small Jellyfish
Small jellyfish eat plankton.
Large Jellyfish
Large jellyfish eat a variety of food. It includes other jellyfish and:
| Fish | Small crustaceans |
| Crabs | Larval shrimps |
How do Jellyfish Prey?
Jellyfish have long, hanging-down tentacles, and their oral arm have stinging cells with spiky barbs. When they float over their prey, they use their stinging and sticky cells to sting and catch the prey. After that, they use their oral arms and tentacles to pull the prey to their mouth.
Do Jellyfish Have Brains and Eyes?
Jellyfish don’t have brains, but have an eye-like structure.
Unlike humans and many other living things, jellyfish don’t have a central brain. Although they don’t have brains, they can learn from their experience with an associated learning process. They use their tentacles as primary sensory organs. Moreover, they also don’t have a heart, bones, or even blood.
Regarding eyes, they have an eye-like structure, i.e., rhopalia. Each rhopalia has four different types of six eyes. Rhopalia acts as a visual information processing center. They use this complex visual structure to see and swim toward a potential habitat.
Jellyfish Aquariums
Jellyfish aquariums are different from regular aquariums. They are cylindrical or cylinder-like structures that allow them to move circularly. They have saltwater LED lights to highlight their transparent bodies.
These tanks have a specially designed flow system. It provides them with an ocean-like habitat. This cross-flow system allows them to keep themselves suspended without settling on the bottom or sticking to the tank’s walls.
What are the Differences between a Jellyfish Tank and a Fish Tank?
A jellyfish tank is different from a regular fish tank. The differences are in the following.
| Features | Fish Tank | Jelly Tank |
| Tank Shape | Usually rectangular | Always cylindrical to avoid sticking in the corners |
| Flow | According to fish species | Gentle and circular, to always keep them suspended |
| Water Quality | Relatively compromisable | No compromise on specific water parameters, zero tolerance for ammonia and nitrite levels |
| Filtration | Little bit compromisable | Aggressive filtration |
| Lighting | According to fish species | Low-light, saltwater LED lights to feature the jellyfish |
| Difficulty | Beginner to advanced, depending on the fish species | Advance |
| Suitable | Fish, invertebrates, and plants | Jellyfish |
The Special Jellyfish
Jellyfish are astonishing sea creatures. Some of them are special regarding their size, venom, and edibility.
The Largest Jellyfish
The lion’s mane jellyfish is the largest known jellyfish. The largest discovered specimen from this species is 120 feet in length from top to bottom. The diameter of the largest lion’s mane jellyfish is 7 feet. They are a weak swimmer. The water current takes them alongside. They have a unique preying style. It attracts potential prey with bioluminescence and catches it with more than 100-foot-long tentacles.
On average, they have up to 1 to 2 feet of bell diameter, and their tentacles can grow 6 to 8 feet long. These jellyfish are present in the colder waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and North Seas. However, they are found around the Chesapeake Bay during early spring and winter.
The Smallest Jellyfish
Irukandji box jellyfish is the smallest jellyfish, with 1 cm. They live in the deep waters of Northern Australia to Western Australia. They usually feed on zooplankton and small crustaceans. On maturation, they can also consume small invertebrates.
Edible Jellyfish
There are some edible jellyfish species, i.e., more than 11. They have a low nutritional value, as their body consists of 5% protein and 95% water. It adds texture to other foods, as they have little flavor. In Asia, i.e., Korea, China, and Japan, people consume it to relieve muscle and bone pain.
Here is a list of some edible jellyfish. There is a thing that is worth considering, some consumers said that they become allergic.
| Rhopilema esculentum (Crystal Jellyfish) | Aurelia aurita (Moon Jellyfish) | Chrysaora pacifica (Pacific Sea Nettle) | Lobonemoides gracilis (Elegant Jellyfish) |
| Rhopilema hispidum (Hairy Jellyfish) | Crambionella orsini (Pink Sea Nettle) | Lobonema smithii (Slender Jellyfish) | Nomura’s jellyfish |
Poisonous Jellyfish
Jellyfish sting their potential prey and then consume it as food. Some of the jellyfish stings are poisonous, and they transfer it to another body. Some of them even prove fatal for humans. Here is a list of such fatal jellyfish species.
Chironex Fleckeri
| Chironex fleckeri is the most fatal jellyfish for humans. About 100 people have died over the last 100 years. These are present near the Australian continent. |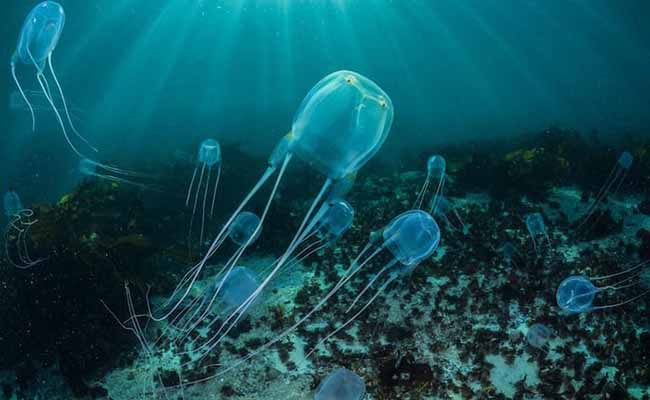  |
Chiropsalmus Quadrigatus
| It’s another lethal fish for humans. Their tentacles can grow up to 8 meters. After their stinging, humans feel pain, respiratory depression, drowning, cardiac dysfunction, and neuromuscular and respiratory paralysis. They are present in the Atlantic Ocean from Brazil to North Carolina. |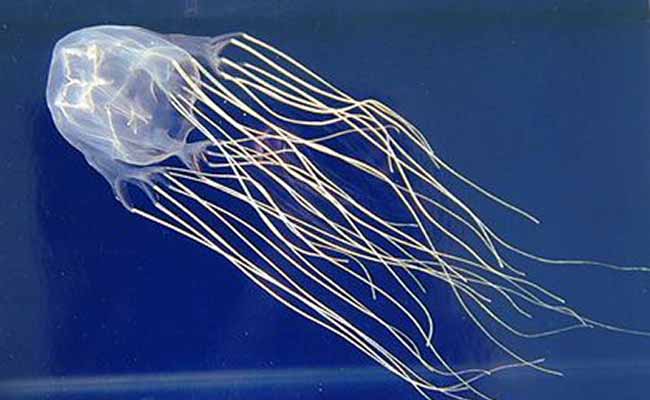  |
Portuguese Man o’ War
| Portuguese Man o’ War is another poisonous jellyfish for humans. They cause severe cutaneous stings and cardiotoxicity in humans. In 1987, a victim of the Portuguese Man o’ War died within a few minutes on Florida’s Atlantic coast. They are present around the world. |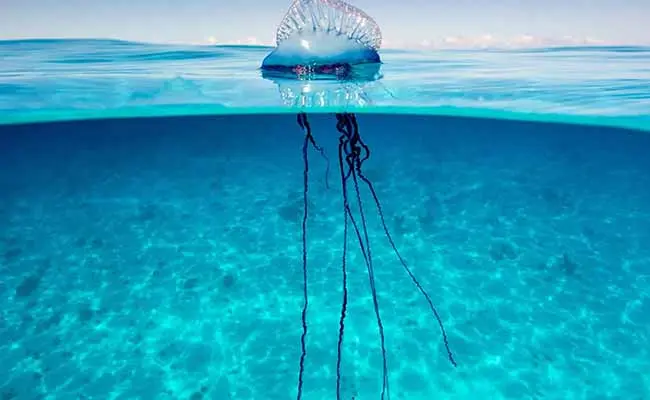  |
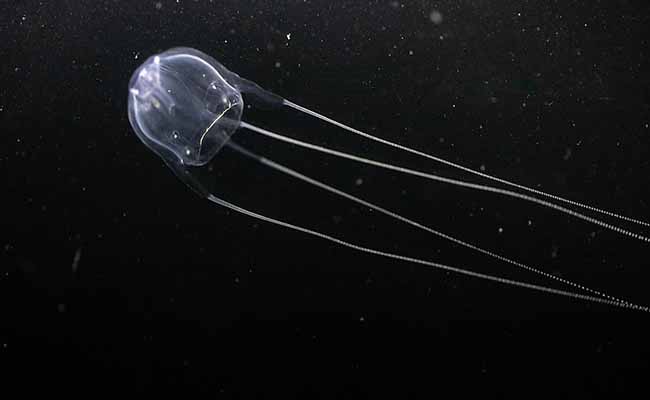
Irukandji Jellyfish
It’s another venomous jellyfish species in the world. When they sting, nothing feels good, but complications begin. Its poison causes the following symptoms:
They are present around Northern Australia. |
 |
Final Thoughts
There are thousands of jellyfish species, and numerous are still undiscovered. What do jellyfish eat? It varies between small and large jellyfish. They don’t have brains but can learn from experience. With the eye-like structure, they find their habitat. Jellyfish aquariums are far different from fish aquariums. Some jellyfish are poisonous, while others are edible. In short, they are awesome.


Leave a comment