Have you ever come across a fish that jumps out of the water, flies like a bird, and has a tail like a manta ray? Flying Fish: This is what we are discussing. The Dynamic fish, with the streamlined and majestic talent of flying in the air, takes us from the depths of the ocean to the sky of nature. But in contrast to the birds that have wings to overcome air resistance, flying fish possess a magic of their own – a power matched by speed, agility, and the unique fins that make them the elite of aerial disappearances.
Content Table
This article is dedicated to the flying fish and how flying fish fly. Let’s explore it in detail.
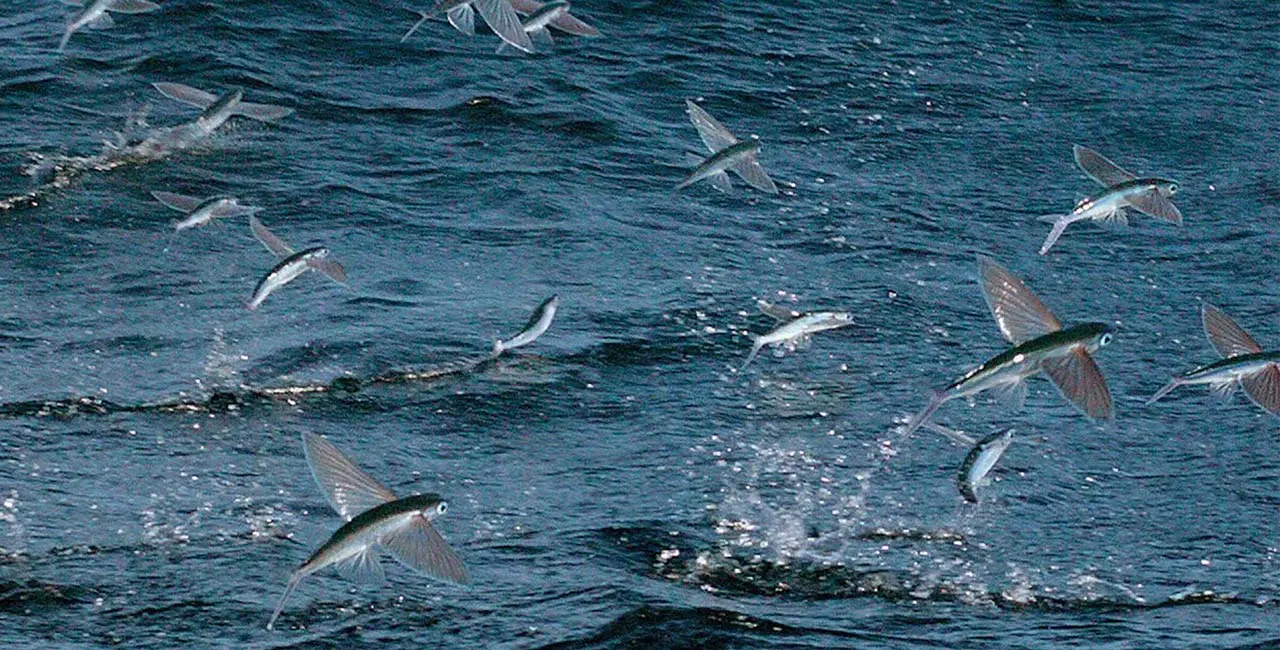

What is Flying Fish?
Flying fish, as the name suggests, represent the Exocoetidae family with more than 64 known species. They are generally ray-finned fish and dwell mostly in warm, tropical, and subtropical waters around the world. These sleek fish have several features that aid their aerial escapades.
Flying fish are the inhabitants of all the earth’s oceans, but they prefer to be there in a moderate and warm subtropical climate. These threshers live close to the water’s surface as they feed on plankton, tiny crustaceans, and small fish.
They are so named because of their unique ability to glide above the water’s surface for short distances. The name “flying fish” perfectly captures this amazing adaptation and sets them apart from other marine species.
Key Features of Flying Fish
- The most striking feature is their massive pectoral fins that spread out like giant wings and enable them to become airborne and glide through the sky.
- These fins are specially modified to help them fly. They can travel long distances above the water to evade predators or catch prey.
- Interestingly enough, flying fish have a streamlined body shape too, which is just one of the key features that aid in overcoming fliers’ resistance and improve their flight capabilities.
- It is quite amazing that the gliders can run fast enough to get into the air and then fly up as far as 400 meters.
- Flying fish utilize specific muscles located in their pectoral fins, which provide exercise while driving and cause changes in the direction of the air as well.
Flying Fish Species
Here are some interesting flying fish species:
1. Sailfin Flying Fish (Cheilopogon Pectoralis)
| Nicknamed the “King of the Gliders” for a reason, the Sailfin Flying Fish holds the record for the longest glide of any fish species, soaring through the air for up to 650 feet (200 meters). These impressive gliders have large, stiff pectoral fins that truly resemble sails, allowing them to catch even the slightest wisp of air to stay aloft. Sailfin Flying Fish are typically found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and their diet consists mostly of plankton and small fish. |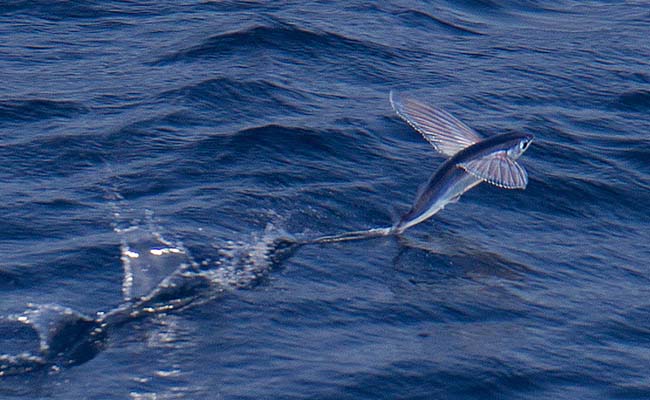  |
2. Spotfin Flying Fish (Cypselurus Exiliens)
| This is one of the most common species of flying fish, easily identified by the distinctive black spots decorating their fins. These spots are thought to help them confuse predators during their aerial escapes. Spotfin Flying Fish are found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world, and they can grow up to about 18 inches (45 cm) in length. They are opportunistic feeders, eating plankton, small crustaceans, and even tiny fish. |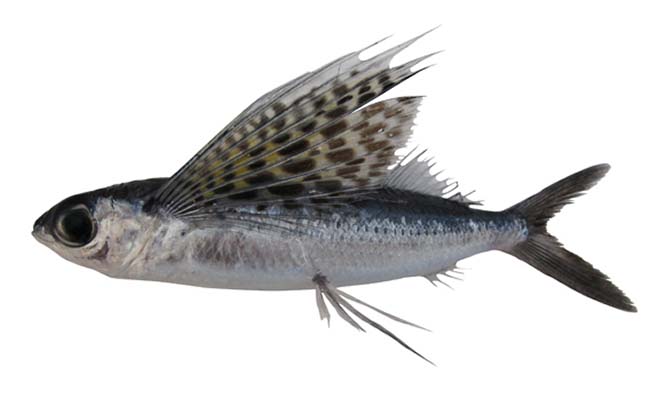  |
3. Atlantic Flying fish (Exocoetus volitans)
| They are also known as two-winged flying fish because only their pectoral fins are enlarged for gliding. This fish is found in the warm waters of the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico. They are also known as two-winged flying fish because only their pectoral fins are enlarged for gliding, reaching lengths up to about 1 foot (30 cm). | 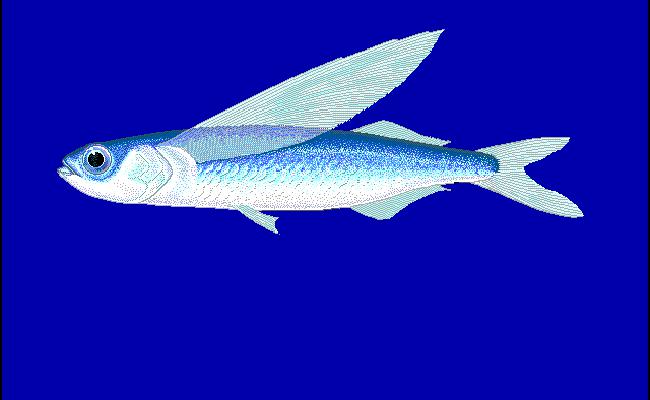 |
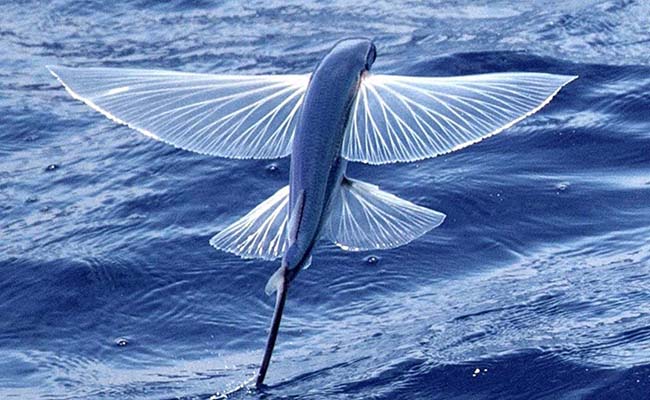
4. California Flying Fish (Cheilopogon Californicus)
| This is a four-winged flying fish, with both pectoral and pelvic fins enlarged, giving them an advantage over their two-winged cousins. This adaptation allows them for more maneuverability and control during flight, making them even more difficult for predators to catch.
California Flying Fish are known for their acrobatics, sometimes changing direction mid-flight with surprising agility. They are found in the eastern Pacific Ocean, off the coast of North America, and can grow up to about 18 inches (45 cm) in length. |
 |
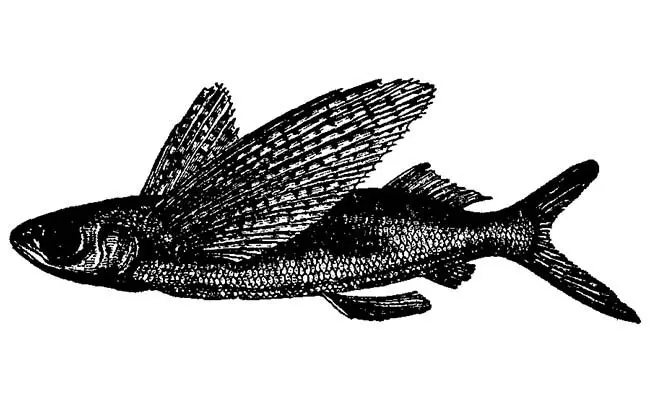
5. Ornamented Flying Fish (Cypselurus Spilonotopterus)
| This aptly named species lives up to its title with a dazzling display of colors and patterns. Its body is adorned with a network of thin, dark stripes running along its back and flanks, while its fins boast a mesmerizing combination of spots and stripes.
These colorful markings are not merely aesthetic; they are thought to play a role in camouflage and communication among Ornamented Flying Fish. They are found in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, and can grow up to about 15 inches (38 cm) in length. Their diet consists mainly of plankton, small crustaceans, and larval fish. |
 |
Why Do Flying Fish Need to Fly
The fish have to fly to save themselves from predators or locate food. They are better suited to glide parallel to the water surface instead of swimming up and down to avoid predators below them. In addition, flying can help to expand their range as they look for plankton and other small organisms that form their diet. This has the additional advantage of air cooling, as it is much cooler than the warm ocean water.
How Do Flying Fish Fly
Flying fish use their specialized fins, which act as wings when they are in motion. The flying fish swims at high speeds near the surface of the water, then launches itself into the air by using its powerful tail fin to propel itself forward. Once in the air, the fish spreads its wing-like fins to catch the wind and glide for distances.
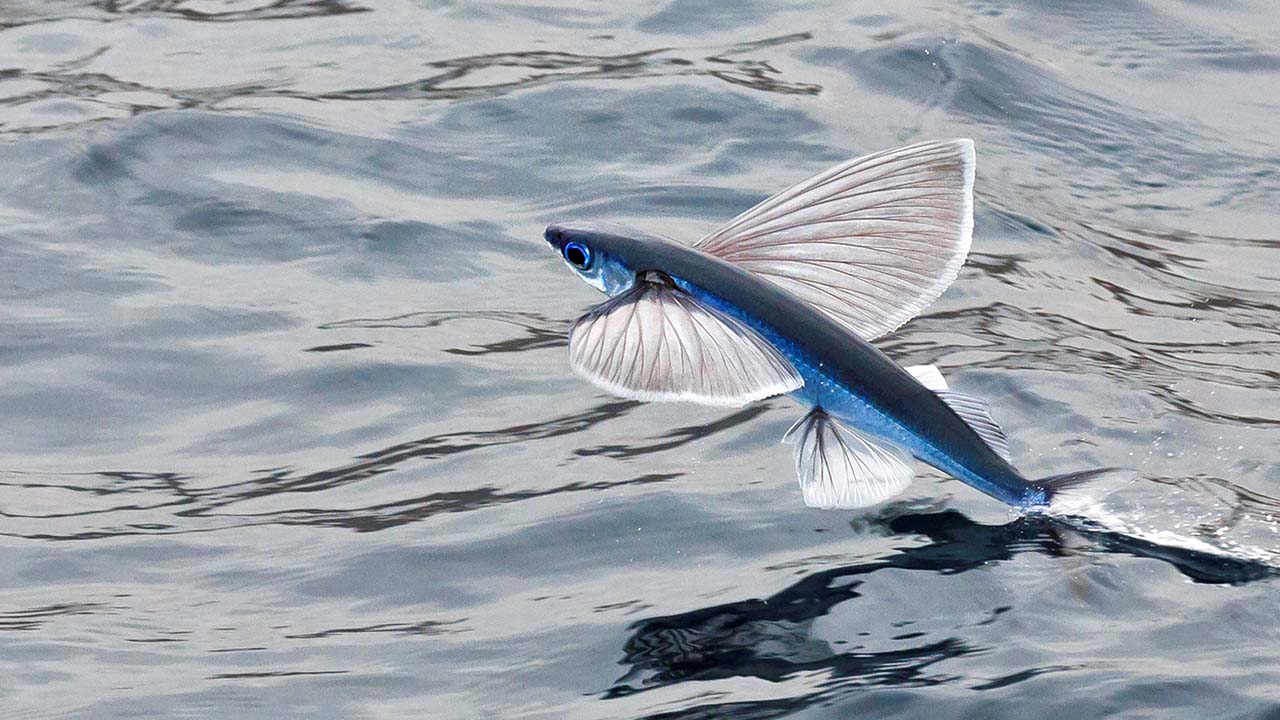
Flying Principle
The principle behind how flying fish fly is similar to how airplanes generate lift. As the flying fish moves through the air, its wing-like fins create lift by generating a pressure difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the fin. This lift allows the fish to stay airborne and glide above the water’s surface. By adjusting the angle of its fins and tail, the flying fish can control its flight path and stay airborne for longer distances.

How Long Can Flying Fish Fly?
Flying fish can stay airborne for some remarkable distances! Depending on the species and wind conditions, they can glide for up to 650 feet (200 meters) at speeds of around 35 miles per hour (56 kilometers per hour). The longest was known to be 1312 feet.
Flying Fish Anecdote
We sailed along on a beautiful day, enjoying the sunshine and the sparkling ocean. Suddenly, there’s a commotion by the deck. A flying fish, maybe a bit too ambitious or startled by something below, launched itself a little too close to the boat. It landed with a surprised flop on deck, right before a sunbathing passenger!
Let’s just say the passenger wasn’t expecting a fishy visitor, and the flying fish probably wasn’t expecting a wooden landing instead of the open sea. There was a lot of flapping, scrambling, and yelling (mostly from the passenger), but luckily, no one was hurt. The crew gently scooped up the bewildered fish and tossed it back into the ocean, much to its relief (and probably the passenger’s secret amusement). It was a moment of chaos and surprise that left everyone with a good story to tell about flying fish anecdotes.


Leave a comment